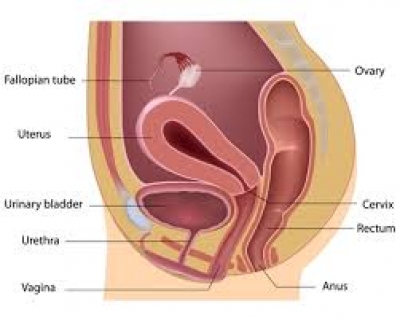
Every month the lining of the uterus is shed during menstrual bleeding. The uterus is nothing but a muscular bag like structure and it contracts and relaxes during periods. The lining of your uterus releases special chemicals called “prostaglandins”. These chemicals increase the strength of the contractions, especially during the first couple of days of a woman’s menstrual cycle. The levels of these chemicals are high during the the first couple of days of periods. High levels of prostaglandins may also cause nausea, diarrhea and lightheadedness.
This “Difficult or painful periods” is called Dysmenorrhea. There are two types of dysmenorrhea; primary and secondary.
- Primary dysmenorrhea is the most common kind of dysmenorrhea. Cramping pain in the lower abdomen (belly) can start from 1–2 days before your period begins and can last 2–4 days.
- Secondary dysmenorrhea is when cramps are a result of a medical problem such as endometriosis. Endometriosis is a condition that occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus is found outside its normal location. This usually causes pain before and/or during a young woman’s menstrual period.
Treatment
If your menstrual cramps are painful, you may want to take an over–the–counter nonsteroidal ant-inflammatory (NSAID) medication for 1–2 days of your period. These medications reduce the prostaglandin chemical which is the cause for your pain. The medication may also reduce your bleeding.
Talk to your doctor before taking any medicine. NSAIDS may cause gastritis and ulcer, so don’t take it if you are suffering from gastritis or prone to it.
Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs), also called birth control pills, as well as other hormonal treatments (patch, vaginal hormonal ring, Depo-provera, IUD and hormonal implants) are often prescribed because the hormones thin out the lining of the uterus which lessens the blood flow and cramping. These medications are sometimes prescribed continuously so you don’t get a period.